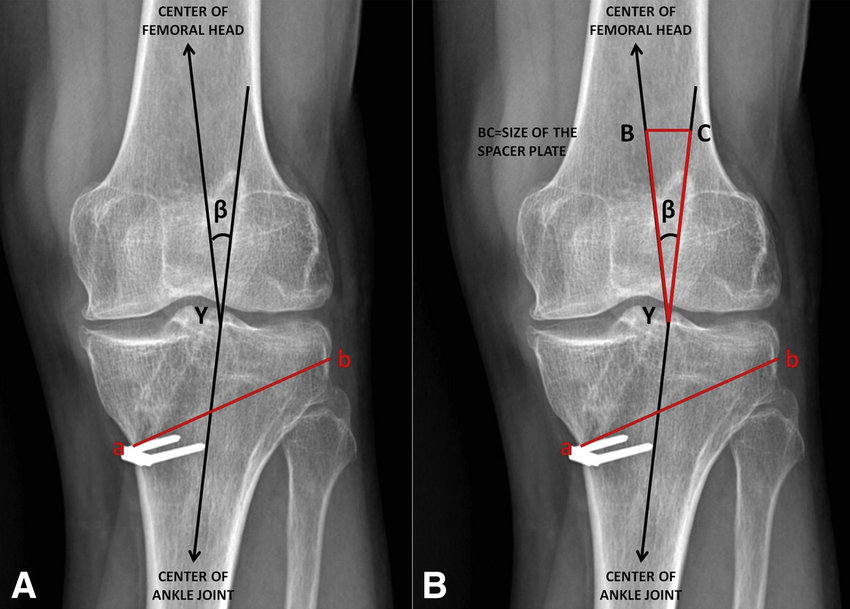
Knee deformity correction through osteotomy is one of the oldest orthopedic procedures. Osteotomy is a technique that through targeted bone resections, with subtraction or addition of bone wedge, produces the variation of the knee axis restoring the correct load and thus limiting the pressure on the worn compartment or preventing wear of the overloaded knee compartment.
The purpose of this intervention is that of a redistribution of the load passing through the joint, thus obtaining a balanced knee with symmetrical load both medially and laterally. Osteotomy literally means bone cutting. During this procedure, the bone is cut and moved, to translate the pressure forces from one side to the other. This procedure is commonly used when knee osteoarthritis involves only one side. The rationale lies in the fact that, by moving the knee axis, the pressure forces acting on the most worn part also shift; in this way, a reduction in pain can be achieved.
What are the symptoms of a patient who is a candidate for a possible osteotomy?
The patient usually complains of pain localized in the worn compartment of the knee associated with functional limitation and physical activity. Endurance sports that raise the pain threshold are often associated with a later onset of the disease.
Who is the typical candidate for knee osteotomy surgery?
The ideal candidate is a young patient, younger than 50 years with an altered axial deviation of the knee such as the varus knee (which produces an overload and elective wear of the inner compartment) or valgus knee (which creates an overload and elective wear of the external sector). In particularly severe cases the indication must be early to limit the damage or premature wear of the cartilage in the overload area.
How is a patient evaluated with overload or localized osteoarthritis of the knee?
- The clinical examination with static as well as a dynamic assessment of the knee axis while stationary and walking.
- Extensive tests such as MRI that show the wear of the cartilage is fundamental.
When is knee osteotomy generally indicated?
It is indicated in the young patient who presents marked wear and tear of a knee compartment associated with axial knee deviation (varus or valgus that is bowlegged or knock-kneed).
It is contraindicated in patients with arthrosis in varus or in valgus that also involves the other compartments of the knee or an excessive axial deviation.
What techniques can be used in knee osteotomy?
Osteotomy can be performed with a subtraction technique (resection of a bone wedge), the addition of a bone wedge with bone graft in the gap or with an external fixator.
The most significant support of the most recent scientific evidence, particularly for young and active patients, is the technique of addition with a dedicated fixation plate.
This technique can be associated with other reparative interventions of the knee such as ligament reconstruction (anterior cruciate ligament) or cartilage transplant, increasing its potential benefit and result for the patient.
The osteotomy intervention, correcting the knee axis and, improves the patient’s condition and functionality in a high percentage of cases (greater than 90%).
The osteotomy then delays the evolution of osteoarthritis by up to a decade. According to scientific evidence, an osteotomy is more appropriate than mono-compartment prosthesis in a patient aged less than 50 years.
Recovery
After about two hours from the end of the operation when the sensitivity of the limb is resumed after the effect of anesthesia is over, pain can be felt. With the regular use of analgesic protocol, it is possible to obtain satisfactory control. After the operation, the patient remains in the surgical ward for a time ranging between 1 and 2 days and will be discharged with a brace to be maintained for 20 days. From the first days, however, the patient begins passive knee flexion-extension exercises, to reduce the risk of stiffness. Achieving a good knee articulation in the early days after surgery is a fundamental factor for having an optimal result. Walking generally begins immediately, with the use of crutches.
High Tibial Osteotomy Cost in India
Tibial osteotomy is a commonly performed orthopedic operation in India. Fortis Memorial Research Institute, Gurgaon and Lilavati Hospital in Mumbai are well known as centers of excellence. Knee osteotomy costs INR 1.2 lakhs or USD USD 1,700 at a top-rated private facility and INR 35,000 or USD 490 at a government hospital.